布夏氏結節(英語:Bouchard’s nodes)是近端指骨關節(手指或腳趾中間的關節)上堅硬的骨頭增生或膠狀囊腫。
常見於手部患有骨關節炎的患者,是由關節軟骨鈣化增生(英語:bone spur)的骨刺形成。


在較少情況中,類風濕性關節炎患者會有這樣的結節,但成因不同,它是因為抗體沉積在關節滑膜(英語:synovium)上引起發炎後的腫脹。
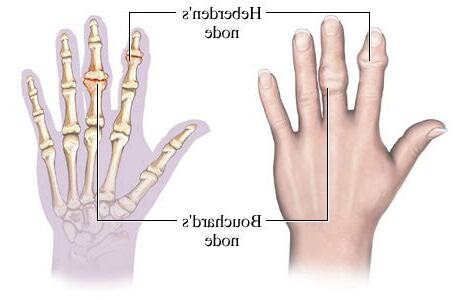
布夏氏結節,等同於骨關節炎增生在遠端指關節(英語:distal interphalangeal joint)的希伯登氏結節[1],但較少見。
布夏氏結節在遠端指關節上的對應表現是希伯登氏結節,但它較為少見。布夏氏結節的影像學表現主要包括指間關節的骨性關節炎和滑膜炎。通過CT掃描,可以清晰地觀察到關節面的微小骨質增生或破壞,以及關節周圍軟組織的不對稱腫脹。
| 疾病 | 部位 | 成因 | 臨牀表現 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 布夏氏結節 | 近端指骨關節 | 關節軟骨鈣化增生 | 結節狀硬塊,伴隨骨性關節炎和滑膜炎 |
| 希伯登氏結節 | 遠端指關節 | 關節軟骨鈣化增生 | 結節狀硬塊,伴隨骨性關節炎和滑膜炎 |
布夏氏結節(英語:Bouchard’s nodes)是近端指骨關節(手指或腳趾中間的關節)上堅硬的骨頭增生或膠狀囊腫。常見於手部患有骨關節炎的患者,是由關節軟骨鈣化增生(英語:bone spur))的骨刺形成。在較少情況中,類風濕性關節炎患者會有這樣的結節,但成因不同,它是因為抗體沉積在關節滑膜(英語:synovium)上引起發炎後的腫脹。布夏氏結節,等同於骨關節炎增生在遠端指關節的希伯登氏結節[1],但較少見。
本文對布夏氏結節進行了簡要介紹,包括其成因、臨牀表現以及與類風濕性關節炎的區別。
布夏氏結節 (Bouchard’s Nodes)
Bouchard’s Nodes are bony growths that develop on the middle joints of the fingers. These nodes are commonly associated with osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide.
Osteoarthritis is a condition that causes the cartilage, which acts as a cushion between bones, to break down. As a result, the bones rub against each other, causing inflammation, pain, and the formation of bony growths like Bouchard’s Nodes.
The exact cause of Bouchard’s Nodes is not fully understood. However, it is believed to be a combination of genetic factors, aging, and repeated stress on the joints. Certain risk factors, such as obesity and previous joint injuries, can also increase the likelihood of developing these nodes.
The most common symptoms of Bouchard’s Nodes include pain and stiffness in the affected joints. The nodes themselves may be tender to touch and can limit the range of motion in the fingers. In severe cases, the nodes can cause deformities and affect the overall function of the hand.
While there is no cure for Bouchard’s Nodes or osteoarthritis, several treatment options are available to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life. These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), physical therapy, splints, and in some cases, surgery.
Prevention and self-care strategies can also play a significant role in managing Bouchard’s Nodes. Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and protecting the joints from excessive stress can help slow down the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of developing new nodes.
In conclusion, Bouchard’s Nodes are bony growths that occur on the middle joints of the fingers and are associated with osteoarthritis. While they can cause pain and stiffness, various treatment options are available to manage the symptoms. By adopting preventive measures and practicing self-care, individuals can take steps to slow down the progression of the disease and improve their overall quality of life.
延伸閲讀…
楊宗翰醫師- 希伯登氏結節- 維基百科
布夏爾結節- 軟骨
