三角形,稱三邊形(英語: Triangle),是三條線段首尾,或不共線三點兩兩連接,組成一個閉合平面幾何圖形,是基本和形。
寫英語字母
A
{\displaystyle A}
、
B
{\displaystyle B}
和
C
{\displaystyle C}
為三角形頂點標號;寫英語字母
a
{\displaystyle a}
、
b
{\displaystyle b}
和
c
{\displaystyle c}
表示邊;
α
{\displaystyle \alpha }
、
β
{\displaystyle \beta }
和
γ
{\displaystyle \gamma }
角標號,或者
∠
A
B
C
{\displaystyle \angle ABC}
這樣頂點標號來表示。
角三角形是其中一角角三角形,其餘兩角於90°。
有一個角是直角(90°)三角形為直角三角形。
成直角兩條稱為「直角邊」(cathetus),直角所對是「斜邊」(hypotenuse);或稱為「弦」,底部稱作「勾」(作「句」),另稱為「股」。
斜邊乘上斜邊上高÷2=勾股相乘÷2=此直角三角形面積(ch=ab)
直角三角形各邊角度關係,可以三角表示。
三角形(稱正三角形),三相等三角形。
三角形具有穩定性,若二個三角形有以下邊角關係定後,它形狀、大小會改變,二個三角形即為全等三角形。


它是鋭角三角形一種。
設其是
a
{\displaystyle a}
,積公式為
a
2
3
4
{\displaystyle {\frac {a^{2}{\sqrt {3}}}{4}}}
。
等腰三角形是三條邊中有兩條相等(或是其中兩隻內角相等)三角形。
等腰三角形中兩條相等稱為「腰」,而另一條稱為「底邊」,兩條腰交叉組成那個點稱為「頂點」,它們組成角被稱為「頂角」。
令其底邊是
b
{\displaystyle b}
,腰是
a
{\displaystyle a}
,積公式為
1
4
b
4
a
2
−
b
2
{\displaystyle {\frac {1}{4}}{b{\sqrt {4a^{2}-b^{2}}}}}
等腰三角形對應高,角平分線和中線重合。
退化三角形是指面積為零三角形。
滿足下列條件之一三角形稱為退化三角形:三個內角度數(180°,0°,0°)或(90°,90°,0°);三其中一條長度0;一條長度於另外兩條和。
有人認為退化三角形並不能算是三角形,這是於它介乎於三角不等式之間,一些資料中否定了其中一條於其餘兩條和情況。
勒洛三角形(英語:Reuleaux triangle),譯作萊洛三角形或弧三角形,稱為劃粉形或曲邊三角形,是圓形以外,易懂勒洛多邊形,一個定曲線。
一個曲線圖放在兩條平行線中間,使這兩平行線,則可以做到:無論這個曲線圖如何運動,只要它是這兩條平行線內,這兩條平行線。
這個定義十九世紀德國工程師弗朗茨·勒洛(英語:Franz Reuleaux)命名。
勾股定理,稱畢氏定理或畢達哥拉斯定理。
言,若直角三角形其中
c
{\displaystyle c}
斜邊,即
c
{\displaystyle c}
對角
γ
=
90
∘
{\displaystyle \gamma =90^{\circ }}
,則
勾股定理逆定理成立,即若三角形滿足
設
R
{\displaystyle R}
為三角形外接圓半徑,則
勾股定理是本定理情況,即角
α
=
90
∘
{\displaystyle \alpha =90^{\circ }\,}
時,
cos
α
=
0
{\displaystyle \cos \alpha =0}
,於是
a
2
=
b
2
+
c
2
−
2
b
c
⋅
cos
α
{\displaystyle a^{2}=b^{2}+c^{2}-2bc\cdot \cos \alpha }
化簡為
a
2
=
b
2
+
c
2
{\displaystyle a^{2}=b^{2}+c^{2}}
。
三角形具有穩定性,若二個三角形有以下邊角關係定後,它形狀、大小會改變,二個三角形即為全等三角形。
三角形判斷有以下幾種:
SSA(Side-Side-Angle、邊、邊、角)不能保證兩個三角形,除非該角於於90°,此時可以保證。
[2]:34[3]
三角形中有著一些線段,是三角形研究對象。
以上線段,每個三角形有三條,且三線共點。
設
Δ
A
B
C
{\displaystyle \Delta ABC\,}
中,若三
a
{\displaystyle a}
、
b
{\displaystyle b}
、
c
{\displaystyle c\,}
中線
m
a
{\displaystyle m_{a}}
、
m
b
{\displaystyle m_{b}}
、
m
c
{\displaystyle m_{c}}
,則:
設
Δ
A
B
C
{\displaystyle \Delta ABC\,}
中,連接三個頂點
A
{\displaystyle A}
、
B
{\displaystyle B}
、
C
{\displaystyle C}
上高分記作
h
a
{\displaystyle h_{a}}
、
h
b
{\displaystyle h_{b}}
、
h
c
{\displaystyle h_{c}}
,則:
設
Δ
A
B
C
{\displaystyle \Delta ABC\,}
中,若三個角
A
{\displaystyle A}
、
B
{\displaystyle B}
、
C
{\displaystyle C}
角平分線
t
a
{\displaystyle t_{a}}
、
t
b
{\displaystyle t_{b}}
、
t
c
{\displaystyle t_{c}}
,則:
三角形內心(Incenter) 、外心(Circumcenter)、垂心(Orthocenter) 及形心(Centroid)稱為三角形四心,定義如下:
關於三角形四心,有這樣一首詩:
外心中點垂線伸,
垂心垂直畫三,
形心角連線中心。
垂心(藍)、形心(黃)和外心(綠)能連成一線,且成比例1:2,稱為歐拉線,九點圓圓心(紅)四點共線,為垂心和形心線段中點。
以下旁心,合稱三角形五心:
設外接圓半徑
R
{\displaystyle R}
, 內切圓半徑
r
{\displaystyle r}
,則:
其中
△
{\displaystyle \triangle }
為三角形面積;
s
{\displaystyle s}
為三角形半周長,
s
=
a
+
b
+
c
2
{\displaystyle s={\frac {a+b+c}{2}}}
三角形面積
A
{\displaystyle A}
是底邊
b
{\displaystyle b}
h
{\displaystyle h}
乘積一半,即:
右圖可知,兩個三角形相拼,可得一平行四邊形。
而該平行四邊形分割填補,能得到一個面積於
b
h
{\displaystyle bh}
長方形。
因此三角形面積
設
a
{\displaystyle a}
b
{\displaystyle b}
為已知兩邊,
γ
{\displaystyle \gamma }
該兩邊夾角,則三角形面積是:
觀察右圖,正弦定義:
此式代入基本公式,可得:
β
{\displaystyle \beta }
、
γ
{\displaystyle \gamma }
為已知兩角,
a
{\displaystyle a}
該兩角夾邊,則三角形面積是:
代入
A
=
1
2
a
b
sin
γ
{\displaystyle A={\frac {1}{2}}ab\sin \gamma }
,得:
注意到
α
+
β
+
γ
=
180
∘
{\displaystyle \alpha +\beta +\gamma =180^{\circ }}
,因此:
海龍公式,其表示形式為:
其中
s
{\displaystyle s}
於三角形半周長,即:
三角形 (triangle) 是邊數形。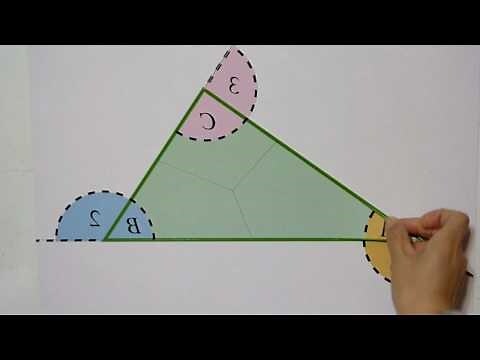
邏輯上,三角形是基本平面圖形,可是四邊形才是人們生活經驗中熟悉圖形。
四邊形可以角線分割成兩個三角形;
反過來,每個三角形是某個平行四邊形角線分割一半,
所以它面積是二分底乘以。
三角形可以細分幾個種類,它們應用上程度,依序為:
直角三角形:Right-angled triangle 或 right triangle。
等腰三角形:Isosceles triangle,其中
兩腰英文是 legs,第三稱為底 base。
兩腰對角稱為底角,底角相等:Two angles opposite the legs (base angles) are equal.
兩腰夾角稱為頂角 (vertex angle 或 apex angle);頂角可能鋭角、直角或角,但底角鋭角。
頂角頂點稱為 apex。
兩腰對角稱為底角,底角相等:Two angles opposite the legs (base angles) are equal.
兩腰夾角稱為頂角 (vertex angle 或 apex angle);頂角可能鋭角、直角或角,但底角鋭角。


延伸閱讀…
三角形:Equilateral triangle,稱為正三角形 (regular triangle)。
有時候正三角形視為等腰三角形特例,有時候規定正三角形並非等腰三角形,這件事並無全球共識,要注意個別文件前提。
鋭角三角形:Acute-angled triangle(三角鋭角)。
角三角形:Obtuse-angled triangle(某一角角)。
斜三角形:Oblique triangle(非直角三角形,鋭角或角三角形)稱 non-right triangle。
規則三角形:Scalene triangle(稱為邊三角形,三,可推論三角)。
我們習慣 \(A\), \(B\), \(C\) 表示三角形頂點,
記作 \(\triangle ABC\),讀作「三角形 ABC」(Triangle ABC)。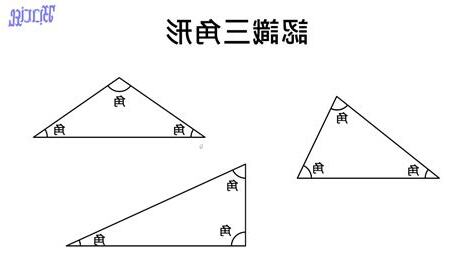
我們同時 \(A\), \(B\), \(C\) 表示內角,
例如頂點 \(A\) 內角記作 \(\angle A\),
讀作「角 A」(angle A)。
我們 \(a\), \(b\), \(c\) 同時表示和邊長,
而 \(a\) 是角 \(A\) 對邊:Side \(a\) is the side opposite angle \(A\)。
沒有聲明時,三角形「角」是指內角 (interior angles)。
三角形內角和定理 (angle sum theorem for triangles)
斷言三個角加在一起於一個平角(俗稱 180 度):
Sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is equal to a straight angle.
此定理可以當作歐氏幾何基本假設,稱為「三角形設準」(Triangle Postulate)。
三角形任一外角 (exterior angle) 是其相鄰內角補角
(the supplementary angle of the corresponding interior angle),
於兩個內角和:
The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the / two
remote / opposite interior angles.
因為空間中共線三點決定一平面,
所以空間中三角形落同一平面上。
[語音講解:triangle.mp3]
[ 回上層 ]
三角形可以細分幾個種類,它們應用上程度,依序為:
直角三角形:Right-angled triangle 或 right triangle。
等腰三角形:Isosceles triangle,其中
兩腰英文是 legs,第三稱為底 base。
兩腰對角稱為底角,底角相等:Two angles opposite the legs (base angles) are equal.
兩腰夾角稱為頂角 (vertex angle 或 apex angle);頂角可能鋭角、直角或角,但底角鋭角。
延伸閱讀…
頂角頂點稱為 apex。
底中線 (median to the base 或者説 median from the apex,即頂點底邊中點決定直線)是等腰三角形對稱軸 (axis of symmetry);
此中線是頂角角平分線 (the angle bisector of the vertex angle),
是底中垂線 (the perpendicular bisector of the base)。
三角形:Equilateral triangle,稱為正三角形 (regular triangle)。
有時候正三角形視為等腰三角形特例,有時候規定正三角形並非等腰三角形,這件事並無全球共識,要注意個別文件前提。
鋭角三角形:Acute-angled triangle(三角鋭角)。
角三角形:Obtuse-angled triangle(某一角角)。
斜三角形:Oblique triangle(非直角三角形,鋭角或角三角形)稱 non-right triangle。
規則三角形:Scalene triangle(稱為邊三角形,三,可推論三角)。
我們習慣 \(A\), \(B\), \(C\) 表示三角形頂點,
記作 \(\triangle ABC\),讀作「三角形 ABC」(Triangle ABC)。
我們同時 \(A\), \(B\), \(C\) 表示內角,
例如頂點 \(A\) 內角記作 \(\angle A\),
讀作「角 A」(angle A)。
我們 \(a\), \(b\), \(c\) 同時表示和邊長,
而 \(a\) 是角 \(A\) 對邊:Side \(a\) is the side opposite angle \(A\)。
沒有聲明時,三角形「角」是指內角 (interior angles)。
三角形內角和定理 (angle sum theorem for triangles)
斷言三個角加在一起於一個平角(俗稱 180 度):
Sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is equal to a straight angle.
此定理可以當作歐氏幾何基本假設,稱為「三角形設準」(Triangle Postulate)。
三角形任一外角 (exterior angle) 是其相鄰內角補角
(the supplementary angle of the corresponding interior angle),
於兩個內角和:
The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the / two
remote / opposite interior angles.
因為空間中共線三點決定一平面,
所以空間中三角形落同一平面上。
[語音講解:triangle.mp3]
[ 回上層 ]
我們習慣 \(A\), \(B\), \(C\) 表示三角形頂點,
記作 \(\triangle ABC\),讀作「三角形 ABC」(Triangle ABC)。
我們同時 \(A\), \(B\), \(C\) 表示內角,
例如頂點 \(A\) 內角記作 \(\angle A\),
讀作「角 A」(angle A)。
我們 \(a\), \(b\), \(c\) 同時表示和邊長,
而 \(a\) 是角 \(A\) 對邊:Side \(a\) is the side opposite angle \(A\)。
沒有聲明時,三角形「角」是指內角 (interior angles)。
三角形內角和定理 (angle sum theorem for triangles)
斷言三個角加在一起於一個平角(俗稱 180 度):
Sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is equal to a straight angle.
此定理可以當作歐氏幾何基本假設,稱為「三角形設準」(Triangle Postulate)。
三角形任一外角 (exterior angle) 是其相鄰內角補角
(the supplementary angle of the corresponding interior angle),
於兩個內角和:
The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the / two
remote / opposite interior angles.
因為空間中共線三點決定一平面,
所以空間中三角形落同一平面上。
[語音講解:triangle.mp3]
[ 回上層 ]
